Artificial Active Immunity Graph
Active immunity - vaccinations A vaccination is the injection of dead or modified microorganisms. Active immunity is defined as immunity to a pathogen that occurs following exposure to all or part of that pathogen.
The white blood cells in your immune system come across the proteins from the viruses bacteria and other foreign elements.

. 344 Recognition of Foreignness 1. Active immunity and passive immunity are two types of adaptive immunity. A dead or weakened form of a bacteria or virus is introduced into the body usually through injection this form of the germ is not able to make us.
This is known as artificial active immunity whereas the kind of immunity that develops when the immune system comes into contact with the infectious agents of disease often making you ill is known as natural active immunity. This is the primary concept behind vaccinations. Your immune system learns about these proteins present in those bacteria and virus cells and creates a protein surface to surround the antigen.
This is when ready-made antibodies from another source are introduced to the body. Provide artificial active immunity. When the body is exposed to a novel disease agent a cascade of signaling molecules and action from the innate immune system results in activation of the adaptive immune system.
Being immune to a disease means that you shouldnt get ill with the same infection again. One vaccinated subject had VZV-specific IgA and IgM in the serum. Artificially acquired active immunity is protection produced by intentional exposure of a person to antigens in a vaccine so as to produce an active and lasting immune response.
Production of large numbers of T cells and B cells. The IFT appears to be a more sensitive. Antibodies are proteins produced by the body to neutralize or destroy toxins or disease-carrying organisms.
For example measles antibody will protect a person who is exposed to measles disease but will have no effect if he or she is exposed to mumps. Define the method by which a host distinguishes itself from nonself foreign materials 2. The bodys lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to the antigens present in the vaccine.
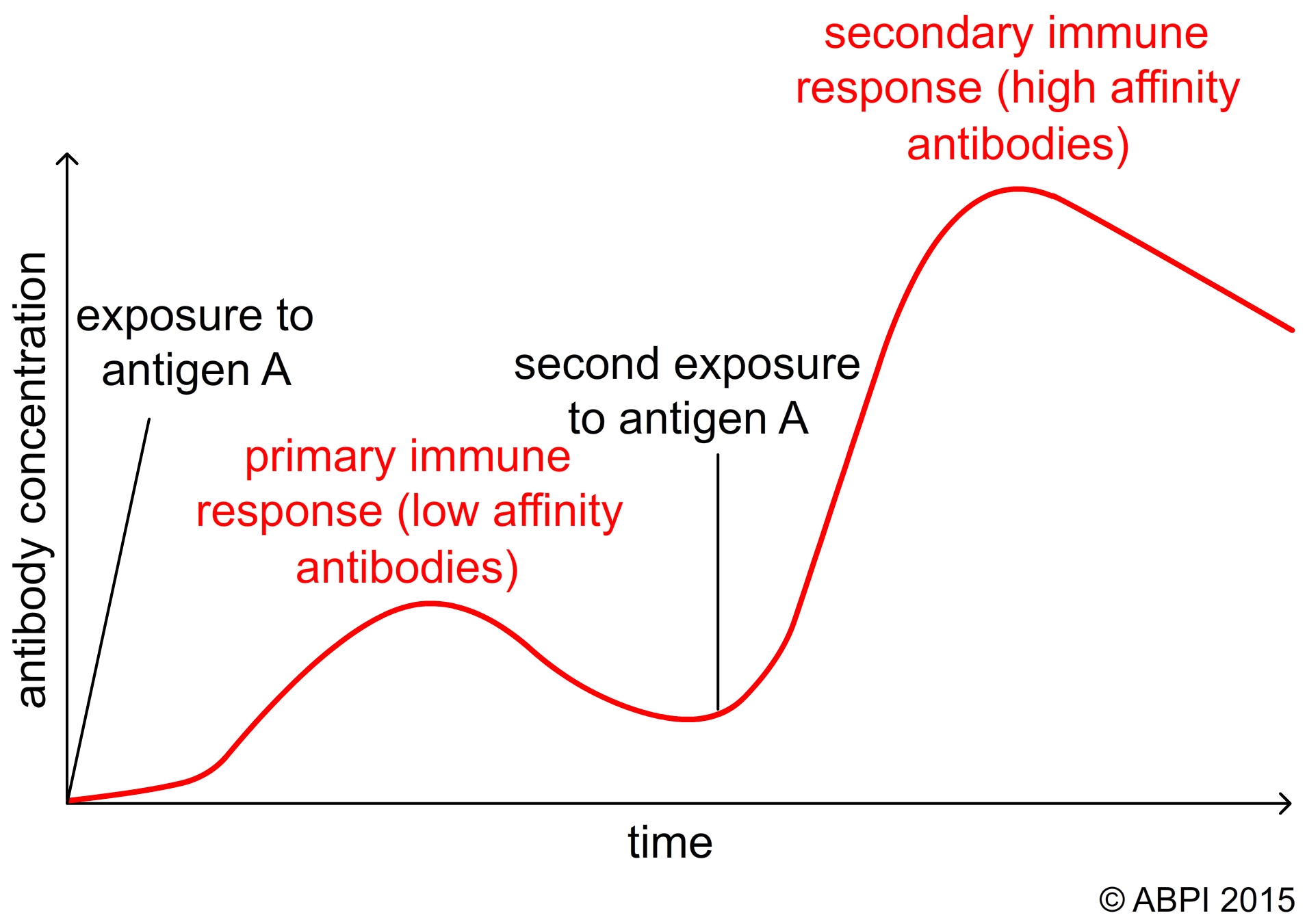
The graph shows what happened to different blood antibody concentrations of the person after vaccination and after infection by the two different pathogens. Provide artificial active immunity. It occurs when we are exposed to a pathogen so that our body can develop a defence against it.
The magnitude of the lymphocyte transformation reaction was higher in the naturally infected than in the vaccinated group P less than 001. ĭ-munĭ-te the condition of being immune. As human or animal blood plasma as pooled human immunoglobulin for intravenous or intramuscular IG use and in the form of monoclonal antibodies MAbPassive transfer is used prophylactically in the case of.
A prominent difference between active and passive immunity is that active immunity is developed due to the production of antibodies in ones own body while passive immunity is developed by antibodies that are produced outside and then introduced into the body. If a virus evolves though you can still catch the new. It encompasses the capacity to distinguish foreign material from self and to neutralize eliminate or metabolize that.
There are two types of immunity. Thus antibody responses to VZV were better in naturally infected than in vaccinated subjects. The primary response when a microorganism enters the body is described as natural active immunity.
Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short-term immunization induced by the transfer of antibodies which can be administered in several forms. Active Immunity Process. A The changes to blood antibody concentration occur because vaccination produces 1 A active artificial immunity B active natural immunity C passive artificial immunity D passive active immunity Mean blood antibody.
Artificially acquired active immunity vaccination intentional exposure to a foreign material Artificially acquired passive immunity preformed antibodies or lymphocytes produced by one host are introduced into another host 11. The antigens in the vaccine stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies and memory cells which are specifically directed against the antigens in the vaccineAfter the immunization if the living. The purpose is to reduce the risk of death and suffering that is the disease.
The protection against infectious disease conferred either by the immune response generated by immunization or previous infection or by other nonimmunologic factors. Artificial induction of immunity is immunization achieved by human efforts in preventive healthcare as opposed to and augmenting natural immunity as produced by organisms immune systemsIt makes people immune to specific diseases by means other than waiting for them to catch the disease.

Nota Latihan Biology Kssm Form 4 Bab 11 3 Weacademia 2021
Artificial Passive Immunity Graph Randytrf

Defense Against Disease Active And Passive Immunity Plantlet

Nota Latihan Biology Kssm Form 4 Bab 11 3 Weacademia 2021
11 1 Defence Against Infectious Disease Bioninja

The Adaptive Immune Response B Lymphocytes And Antibodies Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Comments
Post a Comment